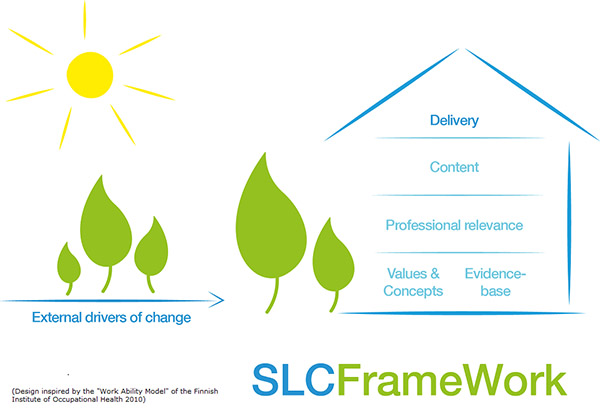
Sustainability values and concepts
“The ultimate goal of education for sustainable development is to impart the knowledge, values, attitudes and skills needs to empower people to bring about the changes required to achieve sustainability. Quality education for sustainable development needs to be based on state of the art knowledge and to continually review and update curricula and teaching materials accordingly. It needs to serve teachers, other professionals and all citizens as life-long learners to respond to society’s challenges and opportunities, so that people everywhere can live in freedom from want and fear, and to make their unique contribution to a sustainable future”. The Lüneburg Declaration on Higher Education for Sustainable Development (p1)[1].
The Lüneburg Declaration (2001) calls on higher education institutions, NGO’s and other stakeholders to:
- Ensure the continual review and updating of learning materials to reflect the latest scientific understanding of sustainability;
- Ensure that the reorientation of teacher education towards sustainable development continue to be given priority as a key component of higher education;
- Provide continuing education to teachers, decision makers and the public at large on sustainable development;
- Encourage all educational institutions to include in their activities a strong component of reflection on values and norms with respect to sustainable development;
- Raise awareness and increase understanding of the importance and relevance of technology assessments and risk assessment;
- Promote the creative development and implementation of comprehensive sustainability projects in higher education, and all other levels and forms of education;
- Increase attention to the international dimension and provide more opportunities for inter-cultural exchange in the learning environment;
- Increase a focus on capacity development and intensified networking among institutions of education; and
- Promote stronger integration of training and research and closer interaction with stakeholders in the development process.
Other declarations will be integrated into the content where relevant. For an overview of relevant declarations see Declarations on higher education and sustainable development.
The concepts and values driving and underpinning this SLC-Framework are, among others, based on concepts set out in The Future Fit Framework published by the UK Higher Education Academy (2012)[2].
Seven key concepts of sustainable development
- Interdependence – of society, economy, and the natural environment, from local to global scales
- Citizenship and stewardship – rights and responsibilities, participation and co-operation
- Needs and rights – of future generations
- Diversity – the importance of cultural, social, economic and biological variety
- Quality of life, equity and justice
- Sustainable change – development and carrying capacity
- Uncertainty and precaution in action
Values
- Sufficiency (living lightly)
- Equity and justice (intragenerational and intergenerational)
- Social inclusion and meeting basic human needs
- Participation and empowerment
- Eco-efficiency (in resource use)
- Biodiversity and green space
- Human rights and needs
- Ethical investment and fair trade
- Sustainable consumerism
- Animal and biocentric rights and needs
- Democracy and participation
- Resource conservation and efficiency
- Community and mutuality
- Meeting needs locally
- Resilience and durability
- System health and well-being
- Futurity (taking the future into account today)
